Proficiency Levels
- FLAD
- Foreign Language Assessment Directory
- Understanding Assessment Tutorial
- Introduction
- Validity
- What do I want to know?
- What skills do I want to measure?
- What is the intended purpose of the test?
- How will I use the test results?
- What information will the test provide?
- Show what you know!
- Puzzle Piece
- Reliability
- What is the relationship between reliability and validity?
- How do I determine if a test is reliable for my situation?
- What could affect reliability?
- Show what you know!
- Puzzle Piece
- Practicality
- Do I have the resources to use this test in my classroom?
- What are the practical considerations for test administration?
- What are the practical considerations in scoring a test?
- Show what you know!
- Puzzle Piece
- Impact
- What are the possible effects of a test?
- What does positive washback look like?
- What does negative washback looks like?
- Who will be affected?
- How will different stakeholders be affected?
- Show what you know!
- Puzzle Piece
- Putting It All Together
- Needs Assessment
- Resources
- Heritage Language Assessment Module
- Introduction
- Linguistic Characteristics and Considerations
- Cultural Characteristics and Considerations
- Factors in Language Development
- Program Types
- Implications for Assessment
- Show What You Know!
- Assessing HLLs: The Why
- Assessing HLLs: The What
- Placement Tests
- Formative Assessment
- Summative Assessment
- Examples of Effective Assessment Tasks
- Summary of Best Practices
- Show What You Know!
- Assessing HLLs: The How
- Needs Assessment
- Selecting Assessments
- Modifying Assessments
- Developing Assessments
- Show What You Know!
- Putting It All Together
- Resources
- Introduction
- Post-Secondary World Language Assessment Module
- Introduction
- Proficiency
- Acquiring Proficiency
- Proficiency Levels
- Proficiency-Based Approach to Assessment: The What
- Proficiency-Based Approach to Assessment: The Why
- Proficiency-Based Approach to Assessment: The How
- Types of Assessments
- Summary of Best Practices
- Show What You Know!
- Placement Testing
- Placement Testing: The Why
- Placement Testing: The How
- Types of Assessment Tools and Approaches for Placement
- Selecting Placement Tests
- Additional Considerations
- Using Placement Test Results
- Summary of Best Practices
- Show What You Know!
- Assessment Plans
- Assessment Plans: The Why
- Assessment Plans: The How
- Aligning Assessment with Instruction
- Performance-based Assessment Tasks
- Designing Performance-based Assessment Tasks
- Scoring Performance-based Assessment Tasks
- Using Integrated Performance Assessments
- Designing Integrated Performance Assessments
- Intercultural Communicative Competence
- Assessing Intercultural Communication
- Assessing Cultures
- Assessment and Program Articulation
- Summary of Best Practices
- Show What You Know!
- Putting It All Together
- Resources
How is proficiency measured in world language courses and programs?
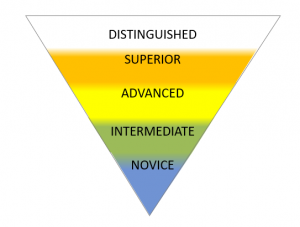 The ACTFL 2012 Proficiency Guidelines are widely used in U.S. college and university world language courses and programs. They provide descriptions of and expectations for speaking, writing, listening, and reading at five main levels of proficiency: Distinguished, Superior, Advanced, Intermediate, and Novice. The Novice, Intermediate, and Advanced levels are further broken down into Low, Mid, and High sublevels.
The ACTFL 2012 Proficiency Guidelines are widely used in U.S. college and university world language courses and programs. They provide descriptions of and expectations for speaking, writing, listening, and reading at five main levels of proficiency: Distinguished, Superior, Advanced, Intermediate, and Novice. The Novice, Intermediate, and Advanced levels are further broken down into Low, Mid, and High sublevels.
Click on each box to learn more about the main ACTFL proficiency levels, and click here to see the full text of the ACTFL Proficiency Guidelines.
At this level, students can understand abstract and technical language on highly specialized topics, as well as different language varieties, dialects, and registers; persuade and hypothesize; and produce language with accuracy and efficiency.
At this level, students can understand precise, specialized vocabulary on a wide range of familiar or less familiar topics; produce longer narrations and more detailed and structured arguments; and accurately and fluently communicate in the language.
At this level, students can understand main ideas and most supporting details on a variety of general interest topics; narrate and describe in past, present, and future time; and produce connected paragraphs to communicate.
At this level, students can understand simple information on familiar or everyday topics; ask and answer simple questions on familiar or everyday topics; and create with language using sentences to communicate.
At this level, students can understand simple words and phrases and use words and short memorized phrases to communicate minimally.
What other frameworks are used to measure proficiency in world language courses and programs?
While the ACTFL Proficiency Guidelines are the most commonly used language proficiency levels in educational settings in the United States, there are other frameworks used to describe language proficiency that it may be helpful for you to be familiar with, including (but not limited to):
- The Common European Framework of Reference (CEFR)
This framework is widely used in Europe and other countries outside the U.S. It provide descriptions of and expectations for language use at six main proficiency levels: A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, and C2.
- The Interagency Language Roundtable Scale (ILR)
- This framework is widely used in the U.S. federal government. It provides descriptions of and expectations for language use at six main proficiency levels: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5.
Language proficiency frameworks can support you in understanding and evaluating what your students can do with the language, and they serve as the foundation of proficiency-based approaches to assessment.
